Norpramin (Desipramine) Patient Information
Find out why Norpramin is prescribed, side effects of Norpramin, Norpramin warnings, effects of Norpramin during pregnancy, more - in plain English.
Generic name: Desipramine hydrochloride
Brand name: Norpramin
Pronounced: NOR-pram-in
Norpramin (desipramine) Full Prescribing Information
Why is Norpramin prescribed?
Norpramin is used in the treatment of depression. It is one of a family of drugs called tricyclic antidepressants. Drugs in this class are thought to work by affecting the levels of the brain's natural chemical messengers (called neurotransmitters), and adjusting the brain's response to them.
Norpramin has also been used to treat bulimia and attention deficit disorders, and to help with cocaine withdrawal.
Most important fact about Norpramin
Serious, sometimes fatal, reactions have been known to occur when drugs such as Norpramin are taken with another type of antidepressant called an MAO inhibitor. Drugs in this category include Nardil and Parnate. Do not take Norpramin within two weeks of taking one of these drugs. Make sure your doctor and pharmacist know of all the medications you are taking.
How should you take Norpramin?
Norpramin should be taken exactly as prescribed.
Do not stop taking Norpramin if you feel no immediate effect. It can take up to 2 or 3 weeks for improvement to begin.
Norpramin can cause dry mouth. Sucking hard candy or chewing gum can help this problem.
--If you miss a dose...
If you take several doses per day, take the forgotten dose as soon as you remember, then take any remaining doses for the day at evenly spaced intervals. If you take Norpramin once a day at bedtime and don't remember until morning, skip the missed dose. Never try to "catch up" by doubling the dose.
--Storage instructions...
Norpramin can be stored at room temperature. Protect it from excessive heat.
What side effects may occur when taking Norpramin?
Side effects cannot be anticipated. If any develop or change in intensity, inform your doctor as soon as possible. Only your doctor can determine if it is safe for you to continue taking Norpramin.
- Side effects of Norpramin may include: Abdominal cramps, agitation, anxiety, black tongue, black, red, or blue spots on skin, blurred vision, breast development in males, breast enlargement in females, confusion, constipation, delusions, diarrhea, dilated pupils, disorientation, dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, excessive or spontaneous flow of milk, fatigue, fever, flushing, frequent urination or difficulty or delay in urinating, hallucinations, headache, heart attack, heartbeat irregularities, hepatitis, high or low blood pressure, high or low blood sugar, hives, impotence, increased or decreased sex drive, inflammation of the mouth, insomnia, intestinal blockage, lack of coordination, light-headedness (especially when rising from lying down), loss of appetite, loss of hair, mild elation, nausea, nightmares, odd taste in mouth, painful ejaculation, palpitations, purplish spots on the skin, rapid heartbeat, restlessness, ringing in the ears, seizures, sensitivity to light, skin itching and rash, sore throat, stomach pain, stroke, sweating, swelling due to fluid retention (especially in face or tongue), swelling of testicles, swollen glands, tingling, numbness and pins and needles in hands and feet, tremors, urinating at night, visual problems, vomiting, weakness, weight gain or loss, worsening of psychosis, yellowed skin and whites of eyes
Why should this drug not be prescribed?
Norpramin should not be used if you are known to be hypersensitive to it, or if you have had a recent heart attack.
People who take antidepressant drugs known as MAO inhibitors (including Nardil and Parnate) should not take Norpramin.
Special warnings about Norpramin
Before using Norpramin, tell your doctor if you have heart or thyroid disease, a seizure disorder, a history of being unable to urinate, or glaucoma.
Nausea, headache, and uneasiness can result if you suddenly stop taking Norpramin. Consult your doctor and follow instructions closely when discontinuing Norpramin.
This drug may impair your ability to drive a car or operate potentially dangerous machinery. Do not participate in any activities that require full alertness if you are unsure about your ability.
Norpramin may increase your skin's sensitivity to sunlight. Overexposure could cause rash, itching, redness, or sunburn. Avoid direct sunlight or wear protective clothing.
If you are planning to have elective surgery, make sure that your doctor is aware that you are taking Norpramin. It should be discontinued as soon as possible prior to surgery.
Tell your doctor if you develop a fever and sore throat while you are taking Norpramin. He may want to do some blood tests.
Possible food and drug interactions when taking Norpramin
People who take antidepressant drugs known as MAO inhibitors (including Nardil and Parnate) should not take Norpramin.
If Norpramin is taken with certain other drugs, the effects of either could be increased, decreased, or altered. It is especially important to check with your doctor before combining Norpramin with the following:
Cimetidine (Tagamet)
Drugs that improve breathing, such as Proventil
Drugs that relax certain muscles, such as Bentyl
Fluoxetine (Prozac)
Guanethidine (Ismelin)
Paroxetine (Paxil)
Sedatives/hypnotics (Halcion, Valium)
Sertraline (Zoloft)
Thyroid medications (Synthroid)
Extreme drowsiness and other potentially serious effects can result if Norpramin is combined with alcohol or other depressants, including narcotic painkillers such as Percocet and Demerol, sleeping medications such as Halcion and Nembutal, and tranquilizers such as Valium and Xanax.
Special information if you are pregnant or breastfeeding
 Pregnant women or mothers who are nursing an infant should use Norpramin only when the potential benefits clearly outweigh the potential risks. If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, inform your doctor immediately.
Pregnant women or mothers who are nursing an infant should use Norpramin only when the potential benefits clearly outweigh the potential risks. If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, inform your doctor immediately.
Recommended dosage for Norpramin
Your doctor will tailor the dose to your individual needs.
ADULTS
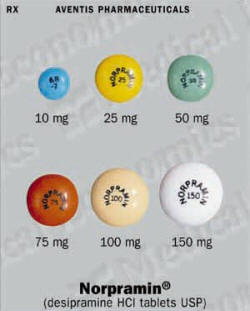
The usual dose ranges from 100 to 200 milligrams per day, taken in 1 dose or divided into smaller doses. If needed, dosages may gradually be increased to 300 milligrams a day. Dosages above 300 milligrams per day are not recommended.
CHILDREN
Norpramin is not recommended for children.
OLDER ADULTS AND ADOLESCENTS
The usual dose ranges from 25 to 100 milligrams per day. If needed, dosages may gradually be increased to 150 milligrams a day. Doses above 150 milligrams per day are not recommended.
Overdosage
Any medication taken in excess can have serious consequences. An overdosage of Norpramin can be fatal. If you suspect an overdose, seek medical help immediately.
- Symptoms of Norpramin overdose may include: Agitation, coma, confusion, convulsions, dilated pupils, disturbed concentration, drowsiness, extremely low blood pressure, hallucinations, high fever, irregular heart rate, low body temperature, overactive reflexes, rigid muscles, stupor, vomiting
Norpramin (desipramine) Full Prescribing Information
Detailed Info on Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Treatments of Depression
Detailed Info on Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Treatments of Eating Disorders
Detailed Info on Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Treatments of ADHD
APA Reference
Staff, H.
(2009, January 3). Norpramin (Desipramine) Patient Information, HealthyPlace. Retrieved
on 2025, November 25 from https://www.healthyplace.com/other-info/psychiatric-medications/norpramin-desipramine-patient-information